1~20 TPD soybean oil refinery plant is preferable for small scale and medium scale oil pressing plant to produce highest quality oils to find more wide applications.QIE Machinery is the leading manufacturer in soybean oil refinery machinery, and has exported a lot of complete soybean oil refinery machine sets to install highly efficient soybean oil refinery plants in the world.
 Processing Capacity: 1-20T/D
Processing Capacity: 1-20T/D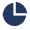 Raw Material: Crude Soybean Oil
Raw Material: Crude Soybean Oil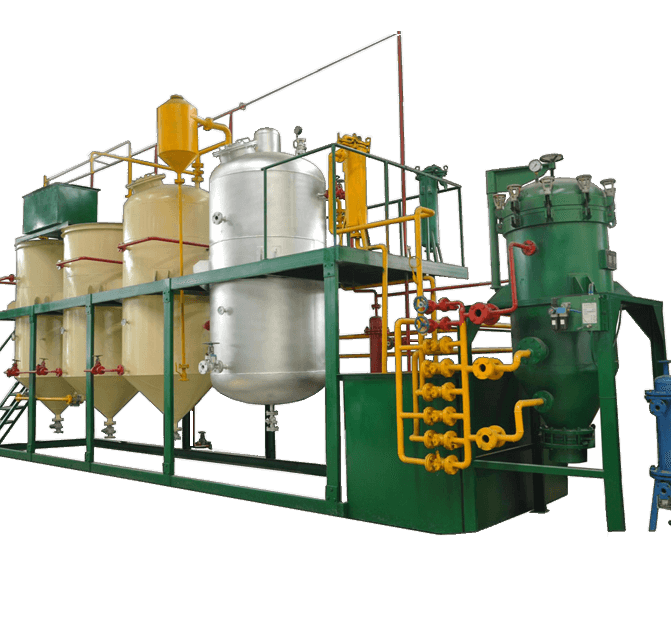



all machine can be customized according to customers' needs.
No matter the crude soybean oil is get by oil press or oil solvent extraction way, it can be refined by the soybean oil refinery machine. The main purpose of soybean oil refinery machine is to separate the impurities in the crude soybean oil based on the different characteristics and enhance the stability and purity of oil. Soybean oil refinery machine includes two technologies, physical refining and chemical refining.
Usually the physical refining is used for the capacity above 30 tons per day. It’s also used when the acid value of crude oil is low. The physical refining is the major methods of soybean oil refinery machine.The physical refining includes three main section, degumming, decolorization and deodorization. The deodorization tower has the function of moving acid and smell, so the acid is moved at the same time of the smell. This is the special part for the physical refinery.
The chemical refining soybean oil refinery machine also has three main sections, degumming and deacidification, decolorization and deodorization. The chemical refining means that it will use chemical in the whole refinery. In fact, only the deacidification section needs the alkali. The decolorization and deodorization are same to the physical way. The chemical way is suitable for small capacity and high acid valued oil.
Both the physical refining and chemical refining can be used in the soybean oil refinery machine. You can choose the appropriate line according to the quality of your crude soybean oil and the capacity.
QIE Machinery, as a premier manufacturer of soybean oil refining facilities in the industry, is committed to delivering clients refined soybean oil plants tailored to their specific needs. We offer a comprehensive suite of services that cover the entire soybean oil refining process, encompassing plant design, equipment selection and production, on-site installation and commissioning, operator training, and more. Here, we present the complete steps of our soybean oil refining production for your consideration and inspiration.
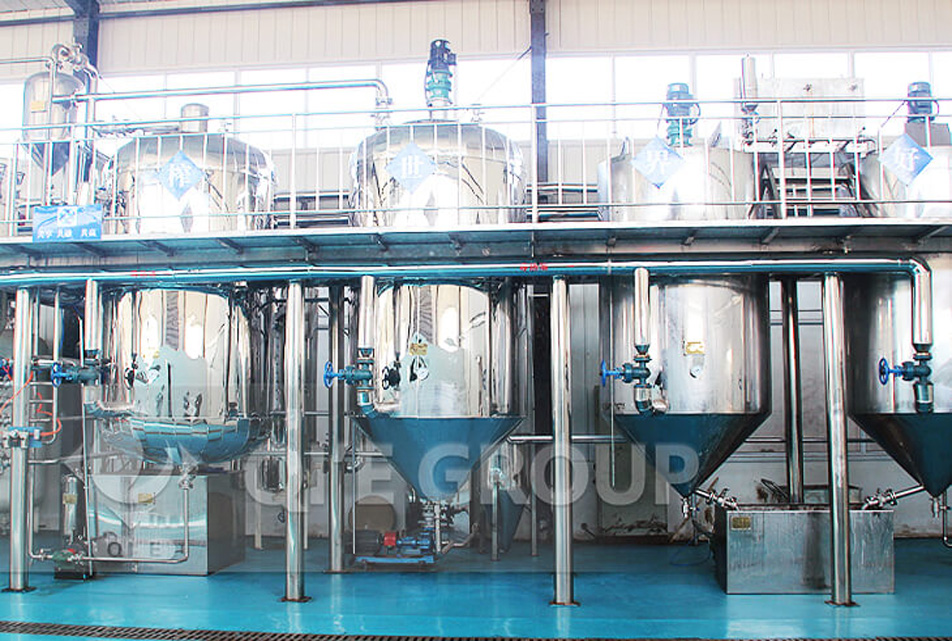

Crude Soybean Oil – Degumming – Deacidification – Decolorizating – Deodorizating – Soybean Oil

Crude soybean oil can be obtained from soybean extraction plant or soybean oil pressing plant. However, crude soybean oil still have some impurities that is insoluble or soluble. For cooking, these impurities must be removed from the crude soybean oil. Detailed process of soybean oil refining is offered below.
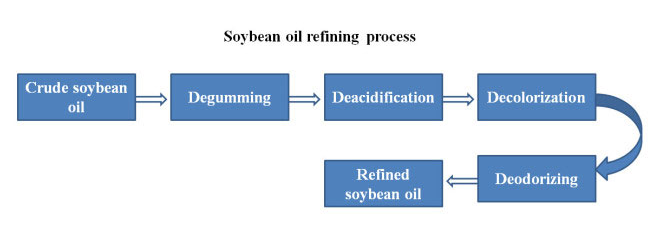
Degumming is to remove impurities, like phospholipid, gum, and protein, and other, by adding hot water or dilute acid, alkali, salt and other electrolyte solution into the crude soybean oil. As a result, the colloidal impurities absorb water, expand and coagulates, finally are separated from soybean oil.
Deacidification is to add alkali to neutralize the free fatty acids (FFAs) and lead to the formation of fatty acid salt (soap) and water. Then, some impurities are absorbed in soap and all sank and separated from the soybean oil.
Decolorizating is to adsorb the pigment and other impurities in crude soybean oil by adsorbents and remove the adsorbents and impurities through filtration to achieve the purpose of decolorization and purification.
Deodorizating is to remove the smelly substance from soybean oil. The most wide used method of deodorization for soybean oil refinery plant is vacuum deodorizating.

Years of development have brought customers from all over the world. Contact us to start customizing a soybean oil production line for your business.






Generally, you need do some preparation, make the project plan, choose soybean oil refinery machine manufacturer, choose soybean oil refining process, etc. Or you can contact with us, and our project manager can guide you step by step. For example, how to decide the workshop location and size, how to choose the suitable refining process based on your budget, etc.
As a professional edible oil refinery plant manufacturer, QIE Machinery can provide you three types soybean oil refinery plant with factory price, according to different input capacities. They are: 1-20tpd batch type soybean oil refinery plant; 20-50tpd semi-continuous type soybean oil refinery plant; 30-1000tpd full-continuous type soybean oil refinery plant.
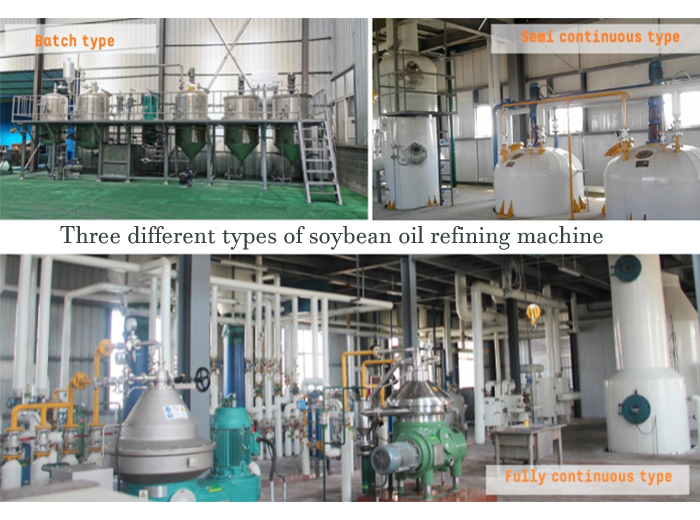

So, you need confirm the input capacity you want. If you have a soybean oil processing plant, you can decide according to the daily output of it. If you want to buy crude soybean oil from others, you need make sure that you have stable daily supply.
As for which type equipment you need choosing, it depends on your requirement of product oil and your budget. For example, if you want to set up a 20tpd soybean oil refinery plant, you can choose batch type or semi-continuous type soybean oil refinery plant. Of course, semi-continuous type has better refining effect, but it costs more.
Our soybean oil production equipment has been exported to more than 120 countries and regions, and many customers have established long-term cooperative relationships with us. Below are some of the soybean oil production equipment and soybean oil production lines we manufacture. Whether you need a single soybean oil production equipment or a complete soybean oil production line, we can customize it for you.
Country : Egypt
Production Output : 300TPD
Raw Materials : Soybean

Country : Egypt
Production Output : 300TPD
Raw Materials : Soybean

Country : Serbia
Production Output : 200TPD
Raw Materials : Soybean
Soybean oil refining uses four sequential machine-driven stages, each with specialized equipment:
Degumming: A degumming tank mixes crude oil with water or dilute acid (e.g., phosphoric acid) to hydrate gums, which are then separated via a centrifuge or filter press. This removes 90–95% of phospholipids.
Neutralization: A neutralization reactor adds a food-grade alkali (e.g., sodium hydroxide) to react with FFAs, forming soapstock (a byproduct used in soap making). A separator removes soapstock from the oil.
Bleaching: A bleaching tower circulates oil through adsorbents (e.g., activated clay, diatomaceous earth) to trap pigments and remaining contaminants. A pressure filter removes spent adsorbents.
Deodorization: A deodorization chamber treats oil with high-temperature steam (220–250°C) under vacuum to vaporize odor compounds, which are condensed and removed. A vacuum pump maintains low pressure to avoid oil oxidation.
Some machines also include a winterization stage (for cold-resistant oil) that cools oil to 5–10°C, crystallizing saturated fats, which are filtered out.
Refinery machines are categorized by production capacity, matching the needs of small to industrial facilities:
Small-scale batch machines (50–200 liters/hour): Compact, manually operated systems where each refining stage is done in batches (e.g., a single tank for degumming, then reused for neutralization). Ideal for artisanal oil mills or local processors.
Medium-scale semi-continuous machines (200–1,000 liters/hour): Modular systems where stages are linked (e.g., degumming → neutralization via conveyor), but some manual transfer is still needed. Used by regional oil brands supplying local markets.
Large-scale continuous machines (1,000+ liters/hour): Fully automated, integrated lines where oil flows continuously through all stages (degumming → neutralization → bleaching → deodorization) without manual intervention. Equipped with PLC controls and in-line sensors, they’re used by industrial facilities supplying bulk oil to food manufacturers or exporters.
Refinery machines are designed to meet strict food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU 1935/2004) through:
Food-grade materials: All parts in contact with oil (tanks, pipes, centrifuges) are made of 304/316 stainless steel, which resists corrosion and doesn’t leach chemicals into oil.
Contamination control: Closed-loop systems prevent air, dust, or foreign particles from entering during refining. Machines also include CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems—automated jets that rinse tanks/pipes with hot water and food-grade detergent between batches.
Process monitoring: In-line sensors measure critical parameters (e.g., FFA levels post-neutralization, color post-bleaching) and alert operators to deviations. For example, if FFA levels exceed 0.1%, the machine pauses neutralization to adjust alkali dosage.
Traceability: PLC systems log batch data (e.g., refining time, temperatures, sensor readings) for 1–2 years, enabling audits and recall tracking if issues arise.
Yes, most refinery machines are versatile but require parameter adjustments to match oil properties:
Sunflower oil: Has higher FFAs (2–3% vs. 1–2% for soybean oil) — increase alkali dosage in neutralization by 10–15% and extend reaction time. Bleaching requires less adsorbent (0.5–1% vs. 1–2%) since sunflower oil has fewer pigments.
Canola oil: Contains more chlorophyll (green pigment) — use additional activated carbon in bleaching (0.2–0.5% of oil weight) to remove color. Deodorization temperature can be lower (200–230°C vs. 220–250°C) to preserve canola’s delicate flavor.
Peanut oil: Has higher gum content — extend degumming time by 15–20% and use a higher water-to-oil ratio (5:100 vs. 3:100 for soybeans) to hydrate gums fully.
Cloudy refined oil:
Cause: Incomplete degumming (gums remaining) or water contamination during CIP.
Fix: Increase water/acid dosage in degumming, extend centrifuge run time, or ensure CIP systems dry tanks fully before use.
Bitter taste in oil:
Cause: Inadequate neutralization (FFAs not fully removed) or soapstock residue.
Fix: Increase alkali dosage, check centrifuge separation efficiency, or add a post-neutralization water wash to remove soap.
Slow deodorization:
Cause: Poor vacuum (leaky seals), clogged steam injectors, or low steam temperature.
Fix: Replace vacuum pump seals, clean steam injectors, or adjust boiler settings to raise steam temperature to 220–250°C.
Excessive oil loss in bleaching:
Cause: Too much adsorbent or clogged filters (trapping oil).
Fix: Reduce adsorbent dosage to 1–2%, replace filter media more frequently, or use a filter press with larger surface area.
Capacity match: Select a machine that aligns with your press output (e.g., a 500 kg/h press needs a 100–110 liter/h refinery machine, accounting for 3–7% yield loss).
Automation level: Manual batch machines are cheaper but require more labor; PLC-controlled continuous machines cost more but reduce errors and labor needs (ideal for 24/7 operation).
Compliance: Ensure the machine meets local food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EU) and has CIP systems for easy cleaning.
After-sales support: Choose a manufacturer that offers local service (critical for repairing centrifuges or vacuum pumps quickly) and a 1–2 year warranty on key components.
Future scalability: For growing facilities, select modular machines that allow adding stages (e.g., winterization) or increasing capacity (e.g., adding a second degumming tank) without replacing the entire system.
Cost vs. value: Avoid the cheapest machines—low-quality stainless steel or inefficient centrifuges will increase maintenance costs and reduce oil quality over time.

QIE Machinery is a large-sizd joint-equity enterprise specializing in the production of soybean oil mechanical equipment. It integrates scientific research, manufacturing and sales, and provides complete set of equipment for soybean oil production. Customize the soybean oil processing equipment capacity according the different customers requirements.