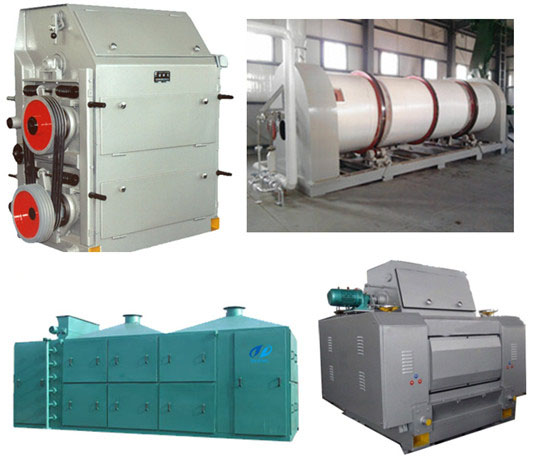
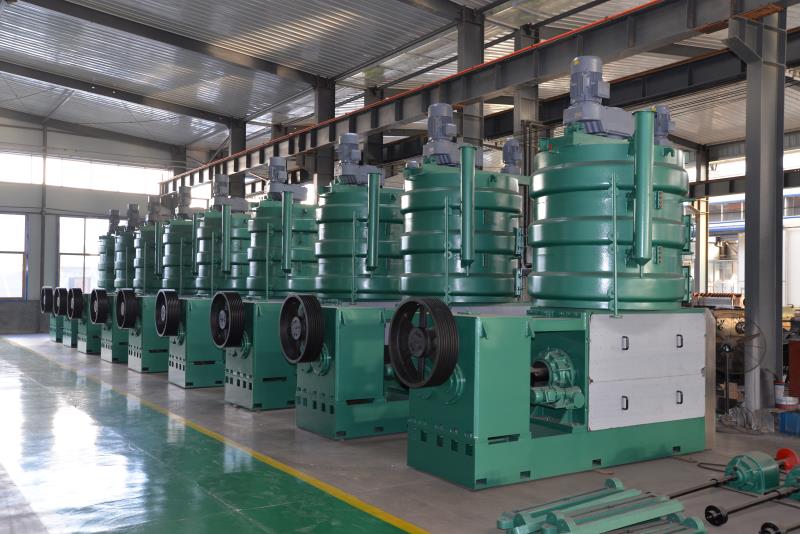
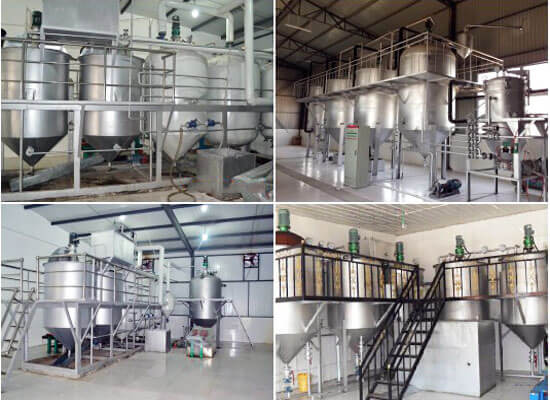
A soybean oil processing mill typically involves several stages: seed cleaning, dehulling, flaking, cooking (or conditioning), pressing/extraction, and refining. The process can vary slightly depending on whether mechanical pressing or solvent extraction is used.
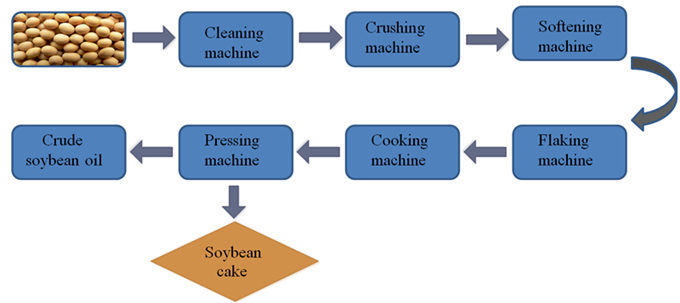
1. Seed Cleaning and Preparation:
Cleaning:
Soybeans are cleaned to remove impurities like stones, dirt, and other debris.
Dehulling:
The hulls (outer layers) of the soybeans are removed, which can improve oil yield and quality.
Crushing/Flaking:
Soybeans are crushed into flakes to increase the surface area for oil extraction.

2. Oil Extraction:
Mechanical Pressing:
The flakes are passed through a screw press, which applies mechanical pressure to extract the oil. This method is often used in smaller-scale operations.

Solvent Extraction:
Soybeans are soaked in a solvent (like hexane) to dissolve the oil. The solvent is then evaporated, leaving the oil behind. Solvent extraction is common in large-scale, high-throughput operations.

3. Oil Refining:
Degumming: Removes phospholipids and other impurities.
Neutralization: Removes free fatty acids.
Bleaching: Removes pigments and other undesirable colors.
Deodorization: Removes volatile compounds that can affect the taste and smell of the oil.

4. Other Processes:
Cooking/Conditioning: Heated and/or steamed to prepare the soybeans for pressing or solvent extraction.
Filtration: Removes any remaining solids from the extracted oil.
Hydrogenation: (Optional) May be used to alter the melting point of the oil for specific applications.
A Business Strategy for Soybean Oil Production
Establishing a soybean oil processing plant for commercial purposes might be a financially rewarding option for those who plan to start a business in the edible oil production line industry. Here, a complete business plan for a soybean oil processing plant is available. It will be very useful to consider these guidelines when starting out. Hence, it’s a good idea to keep these tips in mind.
Raw Material Sourcing and Management:
- Secure reliable soybean suppliers: Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to ensure a consistent and high-quality supply of soybeans.
- Strategic location: Choose a site with easy access to soybean sources, transportation infrastructure, and target markets to minimize distribution costs.
- Inventory management: Implement systems for managing soybean inventory, including proper storage to maintain quality and prevent spoilage.
Production Process Optimization:
- Plant layout: Design a layout that optimizes workflow, minimizes material handling, and ensures efficient production.
- Equipment selection: Invest in high-quality, corrosion-resistant machinery that is specifically designed for soybean oil processing.
- Process control: Implement measures to control temperature, pressure, and other variables during the extraction and refining process to maximize oil yield and quality.
- Safety and environmental compliance: Prioritize safety protocols throughout the production process and adhere to environmental regulations.
- Quality control: Establish a comprehensive quality control system to ensure that the final soybean oil meets the required standards.
Distribution and Marketing:
- Identify target markets: Determine the best channels for distributing soybean oil, including wholesale, retail, or direct-to-consumer.
- Develop a marketing strategy: Create a plan to promote the soybean oil, highlighting its quality and benefits.
- Logistics and delivery: Establish efficient systems for transporting the soybean oil to customers.
Financial Management:
- Cost analysis: Thoroughly analyze the costs associated with setting up and operating the soybean oil production plant.
- Funding options: Explore various funding options, including loans, grants, or private investment, to secure the necessary capital.Conduct a profitability analysis to ensure the business is sustainable and generates a positive return on investment.
Human Resources:
- Staffing: Hire qualified personnel with expertise in soybean oil production, including mechanical engineers, operators, and quality control specialists.
- Training: Provide adequate training to ensure employees understand the production process and safety procedures.
- Employee retention: Implement strategies to retain skilled employees and minimize turnover.





