
Complete soybean oil mill plant is usually designed with seeds pretreatment section, oil processing section, oil refining section and oil filling section. According to oil extraction methods, soybean oil production can be divided into mechanical oil pressing and solvent oil extraction. And crude soybean oil extracted from both mechanical or solvent has impurities and should be refined through a series of oil refining process to get edible refined soybean oil.

Brand
QIE

Raw Material
Soybean

Capacity
10-5000TPD
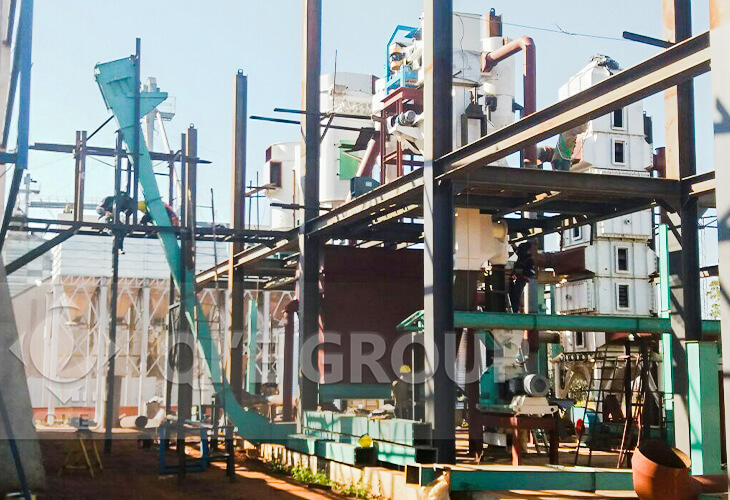


10-5000TPD
Customized Soybean Oil Mill Plant On Demand
Highly Intelligent Production In All Sections
Intelligent

We can offer turnkey soybean oil refinery plant solutions from plant layout design, machinery manufacturing, onsite debugging and installing. The production capacity ranges from 5 ton/d up to 1000 ton/day
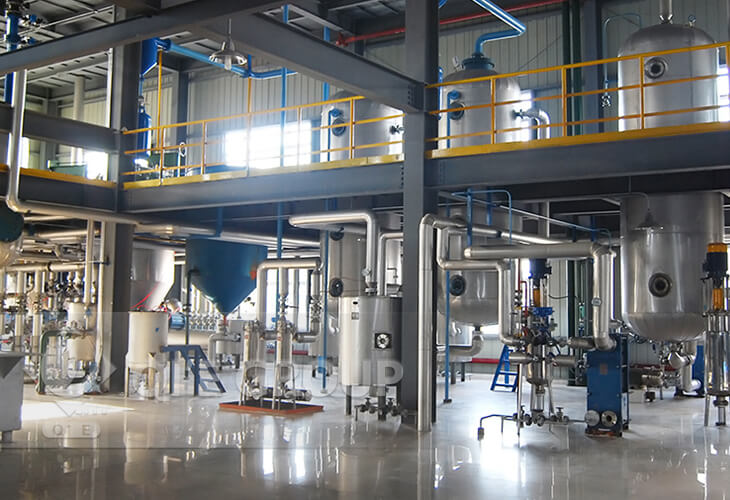


Degumming Process
Some impurity, such as Phospholipid, gum, and protein, can be dissolved into oil when there is no water, but once there is water in oil, these impurities can be dissolved into water. So, in degumming section of soybean oil refinery plant, we use the hot water to wash crude oil for two-three times to remove these impurities.

Neutralizing/Neutralization Proces
The crude oil is fed into the neutralizer and mixed with small amounts of degumming agent such as phosphoric acid to help remove gums.Free fatty acids are removed from the oil by adding caustic soda and heating it at 60˚ then stirring the mixture. Heating forms soap base, which is then precipitated and collected, and washed with water to remove alkaline particles.

Decolorizing Process
The neutralized oil requires bleaching machine to get rid of colors. This is done by adding the oil in a bleacher machine whereby it is heated to remove any moisture it might have and then mixed with earth bleach and activated carbon. These two properties absorb any colors after which the oil is passed through a filter to separate oil from earth bleach and carbon. The result is golden light oil.

Deodorizing Process
The golden light oil has unpleasant odors which result from materials such as aldehydes, ketones, tocopherols and phenols among other odiferous elements. Deodorizing process of soybean oil refinery plant helps remove these odors by adding the oil in the deodorizer and heating it above at very high temperature and under very high vacuum. This deodorizing process helps get rid of all odors.

QIE Grain and Oil Machinery Co., Ltd
With decades of expertise,QIE Machinery has successfully installed soybean oil production lines worldwide, serving customers in over 100 countries. Our extensive product portfolio includes soybean oil and soybean protein production solutions, as well as customized solutions for specific capacities ranging from small-scale operations to large conglomerate production facilities.
Whether in Asia, Europe, the Americas or Africa, our equipment is tailored to meet local market needs and production challenges. We operate worldwide and customer satisfaction is at the heart of every project we undertake. From initial consultation and design to installation and after-sales service, QIE Machinery ensures that every solution meets the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Get Quote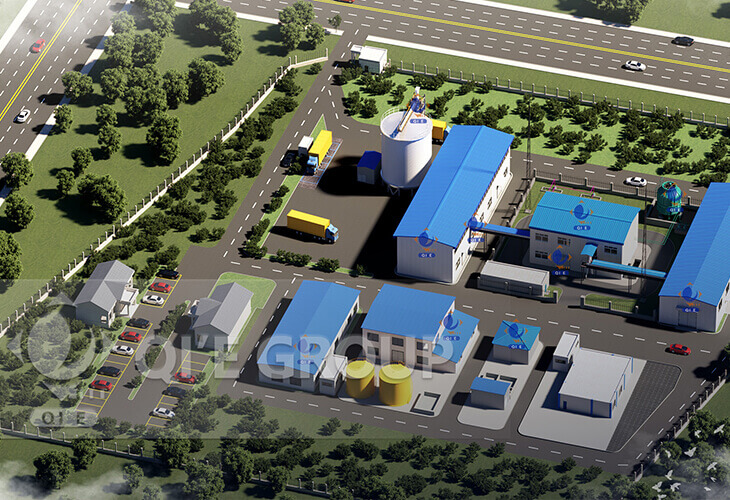

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+30TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More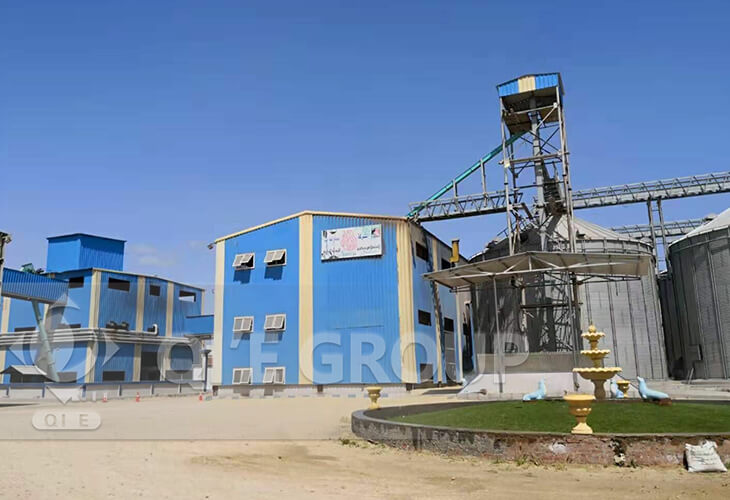

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+60TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More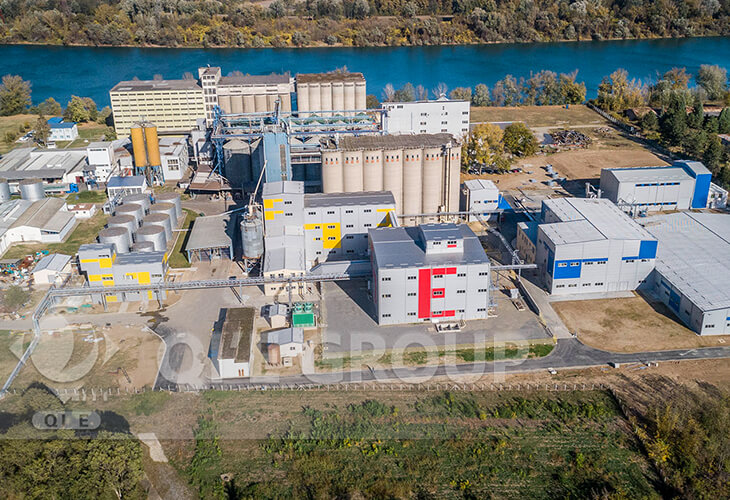

This is our soybean protein isolate project with low temperature desolventing technology in Serbia.
Learn More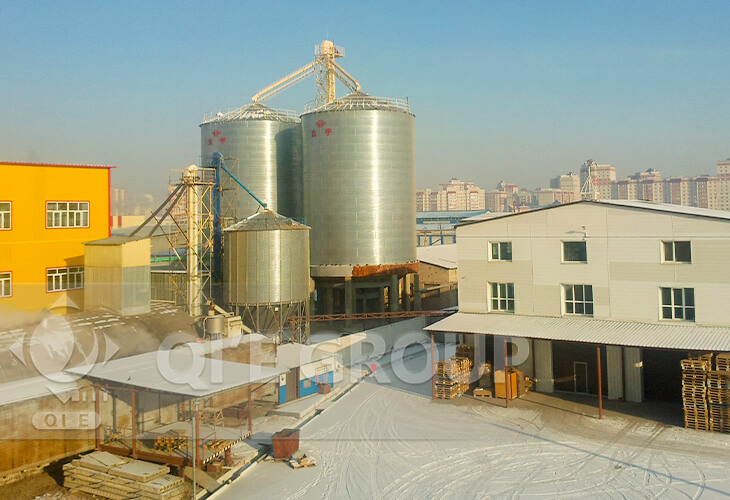

The 200TPD soybean oil project is for our Russian customer.The workshop adopts pretreatment, solvent extraction and refining process.
Learn MoreA basic (small to medium-scale) soybean oil mill plant requires:
High-quality soybeans are critical for efficient oil production.
Oil content: 18–22% (varies by variety; high-oil soybeans are preferred for better yield).
Moisture content: 10–12% (too high causes mold; too low reduces press efficiency).
Purity: Less than 2% impurities (stones, dirt, broken seeds) to avoid equipment damage and oil contamination.
Quality: No mold, mycotoxins, or excessive foreign matter. Freshly harvested soybeans (stored properly) yield better oil than old stock.
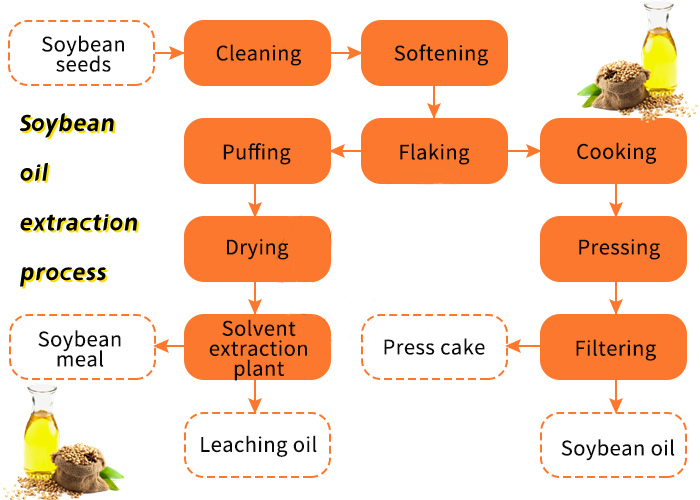
Soybeans contain 18–22% oil, but actual yield depends on the extraction method:
Refining transforms crude soybean oil (dark, with impurities) into clear, edible oil. Steps include:
Refining is necessary to meet food safety standards, improve stability (resist oxidation), and enhance consumer acceptability (color, taste, odor).
The primary by-product is soybean meal—the solid residue after oil extraction, containing 40–48% protein. It is:
Other by-products:
Mill plants must address waste, emissions, and resource use:
Wastewater: From cleaning and refining, containing organic matter. Treated via settling tanks, biological filtration, or anaerobic digestion to meet discharge standards.
Solid waste: Soybean meal and hulls are recycled as feed or fuel; filter residues are composted.
Emissions: Solvent extraction plants recover hexane (a volatile solvent) to prevent air pollution. Boilers use low-sulfur fuel or biomass (hulls) to reduce greenhouse gases.
Resource efficiency: Water recycling (for cleaning), heat recovery (from solvent evaporation), and energy-efficient motors minimize environmental impact.
Regulations vary by region but typically include:
Food safety certifications: Compliance with FDA (U.S.), FSSAI (India), or EU standards for edible oil, ensuring low contaminants and safe processing.
Environmental permits: For wastewater discharge, air emissions, and waste management.
Safety protocols: Guards on machinery, fire prevention systems (especially in solvent areas), and worker training in handling equipment and chemicals.
Quality control: Regular testing of oil (for purity, acidity, contaminants) and meal (for protein content) to meet market standards.
Business licenses: Registration as a food processor, tax compliance, and adherence to labor laws.