
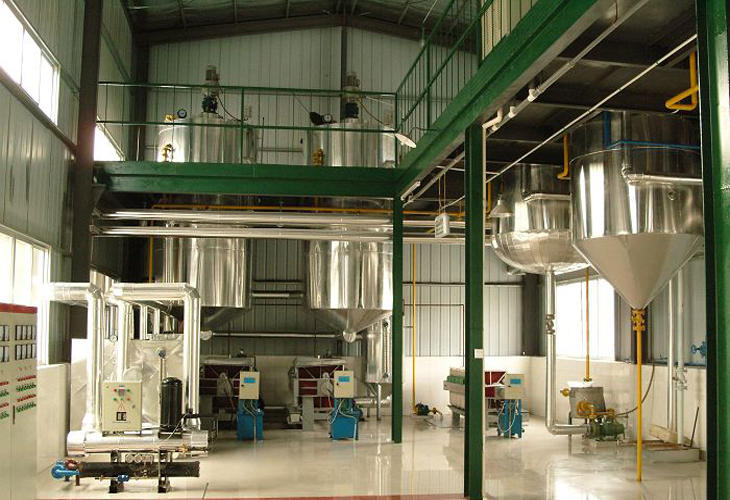
The crude soybean oil obtained from soybean oil expellers or solvent extraction contains impurities such as phosphatides, free fatty acids (FFA), pigments, off-flavor, etc. Oil Refining is a series of process to remove these impurities. After refining, the flavor, color, and smell of oil is improved, the stability is improved which is good for long time storage, the smoke point of oil is increased. We provide 1-10T/D soybean oil refinery plant for you. .

Brand
QIE

Raw Material
Crude Soybean Oil

Capacity
1-10TPD


1-10TPD
Customized 1-10T/D Soybean Oil Refinery Plant On Demand
Highly Intelligent Production In All Sections
Intelligent
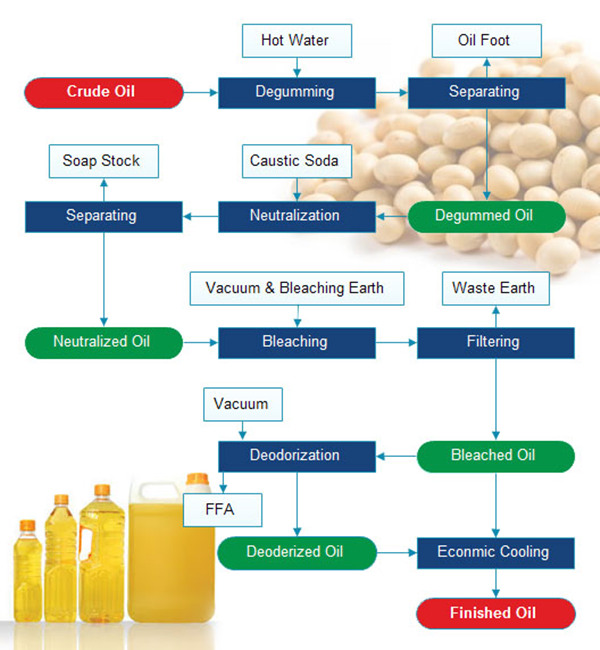

Refining is essential to improve the oil’s taste, smell, color, and stability, ensuring it meets market standards. Soybean oil refining plants can be tailored for first and second-grade oil production. The total refinery plant contains refining pot, decolorizing pot, deodorizing pot, steam generator, heat conduction furnace, etc.
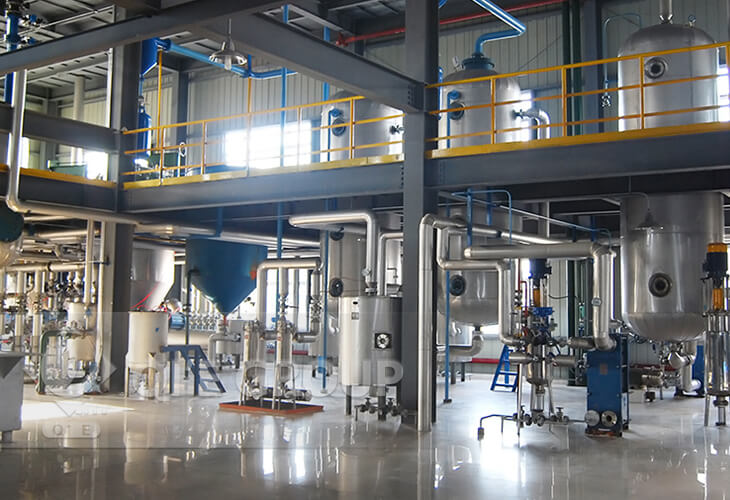


Batch Oil Refinery Line 1-20TPD
Batch oil refinery is one of the main kinds of oil refinery methods, which is suitable for various vegetable and animal oils, such as soybean oil, peanuts oil, sunflower oil, rape seeds oil, cottonseeds oil, coconut oil, palm oil, niger seeds oil, rice bran oil, fish oil, seal oil, etc. It is suitable for small capacity, 1TPD to 20TPD, which contains Degumming, Neutralizing, Decolorization and Deodorization section. As a result, it can also be called small edible oil refinery unit.

Continuous Oil Refinery Plant >30TPD
Continuous Type Oil Refinery Plant is recommended against the batch refining for higher capacity plants above 30 tons per day and for oils containing higher FFA content. This process line is bit expensive than batch oil refinery process but it provides superior quality refined oil along with automation system and low processing cost. It is also a large edible oil refinery unit.

Semi-Continuous Oil Refinery 10-50TPD
The semi-continuous oil refinery process design is based on batch type but higher than batch type. Semi-continuous oil refinery process needs less investment cost. The semi-continuous oil refinery capacity can be designed according to customer requirement. It's suitable for the middle type oil refinery plant from 10TPD to 50TPD. So it is also called middle scale oil refinery unit.

What capacity can QIE Machinery offer?
1TPD,2TPD, 3TPD, 5TPD,10TPD,15TPD, 20TPD, 30TPD (batch Design)
15TPD,20TPD.30TPD;(semi-Continuous Design)30TPD ,50TPD,100TPD,200TPD,400TPD (continuous Design)
Soybean oil refinery plant is to remove harmful impuries, such as protein, phospholipid, pigment, moisture, wax and other impurities. And then the refined edible oil can reach the standard of food and storage.

QIE Grain and Oil Machinery Co., Ltd
With decades of expertise,QIE Machinery has successfully installed soybean oil production lines worldwide, serving customers in over 100 countries. Our extensive product portfolio includes soybean oil and soybean protein production solutions, as well as customized solutions for specific capacities ranging from small-scale operations to large conglomerate production facilities.
Whether in Asia, Europe, the Americas or Africa, our equipment is tailored to meet local market needs and production challenges. We operate worldwide and customer satisfaction is at the heart of every project we undertake. From initial consultation and design to installation and after-sales service, QIE Machinery ensures that every solution meets the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Get Quote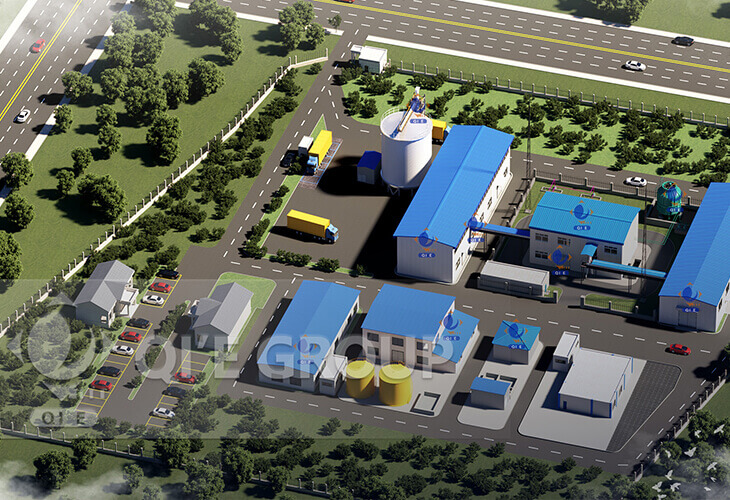

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+30TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More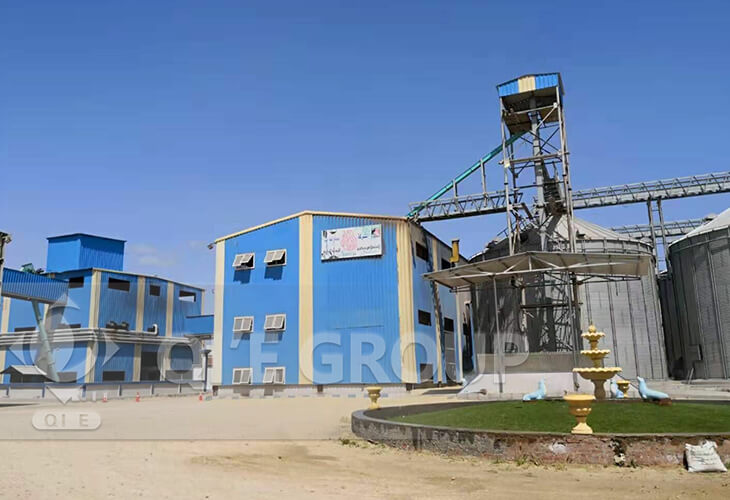

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+60TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More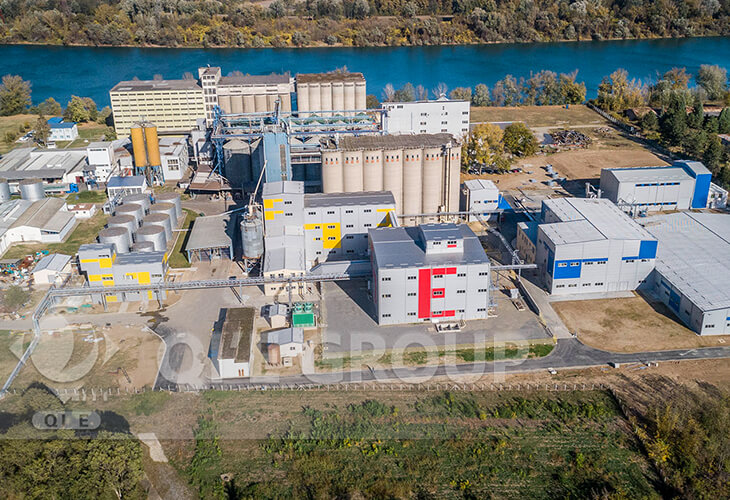

This is our soybean protein isolate project with low temperature desolventing technology in Serbia.
Learn More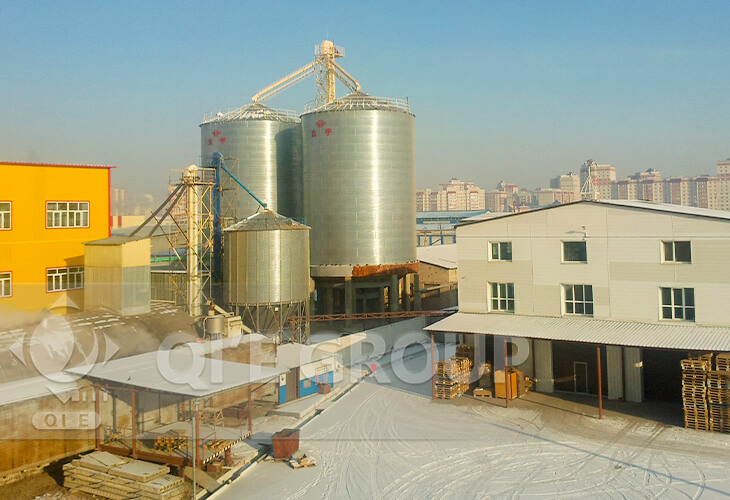

The 200TPD soybean oil project is for our Russian customer.The workshop adopts pretreatment, solvent extraction and refining process.
Learn MoreSoybean oil refining typically involves four core stages, each targeting specific impurities:
Degumming tanks: Mix crude oil with water/acid and agitate to form gums.
Centrifuges or separators: Separate gum sludge from oil after degumming and soapstock after neutralization.
Neutralization reactors: Mix oil with alkali and control temperature/pH for FFA removal.
Bleaching vessels: Sealable tanks for mixing oil with adsorbents under controlled heat and vacuum.
Filter presses or leaf filters: Remove spent adsorbents from bleached oil.
Deodorization columns: Tall, vertical vessels where oil is heated under vacuum, and steam is injected to strip volatile compounds.
Heat exchangers: Recover heat from deodorized oil to preheat incoming oil, reducing energy use.
Storage tanks: Stainless steel tanks for crude oil, intermediate products, and refined oil, often with temperature control and nitrogen blanketing to prevent oxidation.
Small-scale refineries (processing 1–5 tons of crude oil/day): Use batch processing with manual or semi-automated equipment (e.g., small bleaching tanks, manual filters). They often skip deodorization or use simplified versions, producing oil for local markets.
Medium-scale refineries (5–50 tons/day): Employ semi-continuous processing with automated controls for temperature and mixing. They include all four refining stages and serve regional food manufacturers.
Large-scale refineries (50+ tons/day): Use fully continuous, computer-controlled lines with high-capacity centrifuges, multi-stage bleaching, and advanced deodorization systems. They produce oil for national/international markets and meet strict quality standards (e.g., Codex Alimentarius).
Refined soybean oil must adhere to global and regional standards, including:
Enforcement involves in-plant testing (using titration for FFAs, colorimeters, and spectrometers) and third-party audits. Regulatory bodies like the FDA (U.S.), EFSA (EU), or FSSAI (India) conduct inspections to ensure compliance.
Energy use depends on scale and process intensity:
Large refineries often use heat recovery systems (e.g., capturing heat from deodorized oil to preheat incoming oil) to reduce energy consumption by 20–30%. Some also integrate biomass boilers (using soybean hulls or meal waste) to lower reliance on fossil fuels.
Waste streams are managed to minimize environmental impact and recover value:
Oil oxidation: Occurs if refining temperatures are too high or exposure to air is excessive. Mitigated by using nitrogen blanketing in storage tanks and optimizing deodorization time/temperature.
Off-colors/flavors: Caused by incomplete bleaching or deodorization. Solved by adjusting adsorbent dosage in bleaching or increasing steam injection in deodorization.
Emulsions (in degumming/neutralization): Form when oil and water mix excessively, making separation difficult. Prevented by controlling temperature and agitation speed, or adding demulsifiers.
High energy costs: Reduced via heat recovery systems, efficient vacuum pumps, and optimizing process timelines (e.g., shorter deodorization cycles with better steam distribution).
Yes, most refineries can process other oils (e.g., canola, sunflower, palm) with minor modifications:
Multi-oil refineries are common in regions with diverse vegetable oil production, as they maximize facility utilization.
Costs vary significantly by scale:
Key cost drivers include equipment quality (stainless steel vs. mild steel), automation level (manual vs. PLC-controlled), and compliance with environmental/regulatory standards.